- Kyiv School of Economics
- About the School
- News
- KSE Institute Russia Chartbook – July 2025: Budget deficit continues to grow; low oil prices are a major challenge
KSE Institute Russia Chartbook – July 2025: Budget deficit continues to grow; low oil prices are a major challenge
29 July 2025
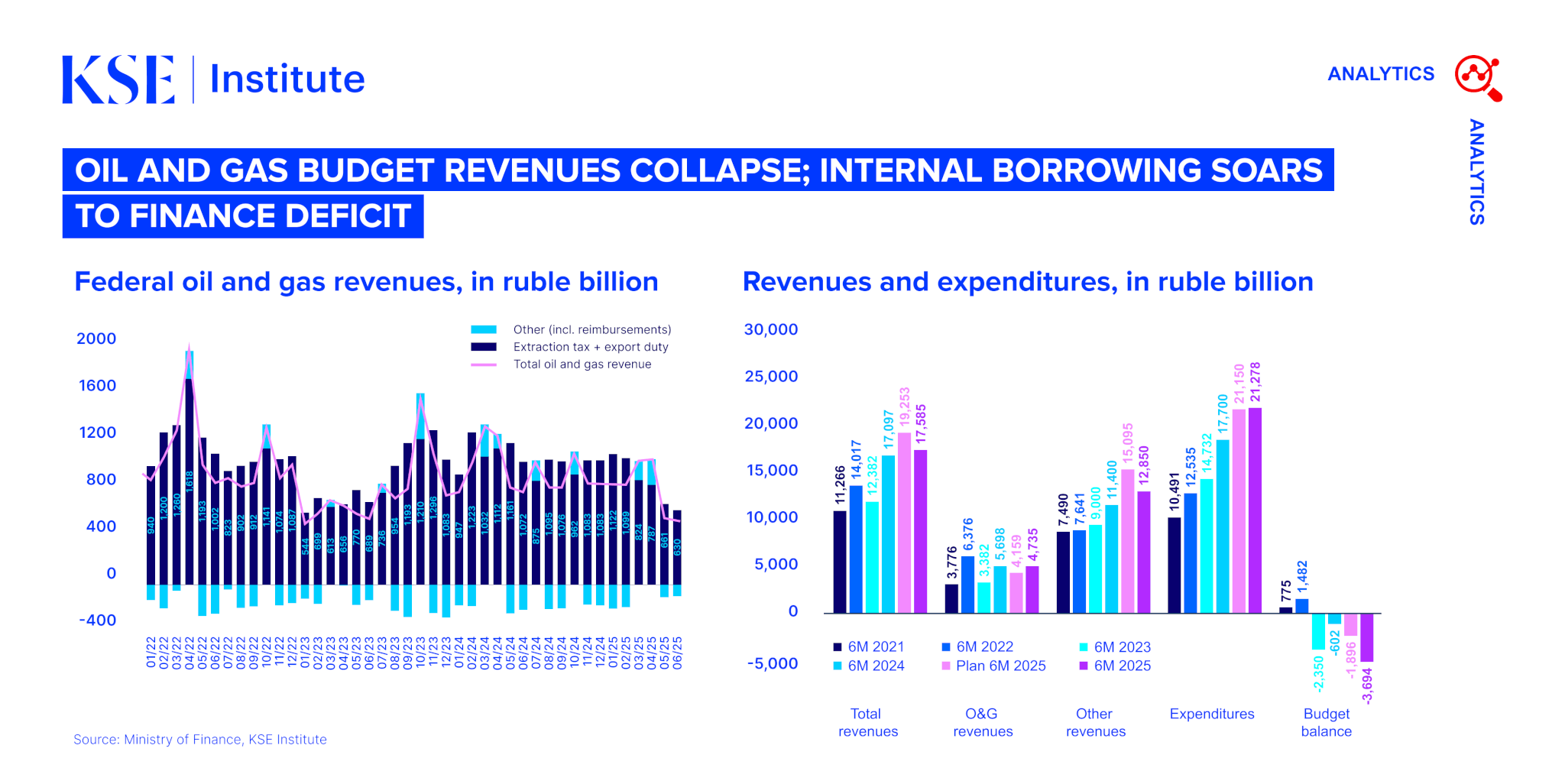
KSE Institute has published the July edition of its Russia Chartbook: “Budget deficit continues to grow; low oil prices are a major challenge.” Russia’s deepening fiscal and economic challenges provide an opportunity for Ukraine’s allies to intensify sanctions and financial pressure, further limiting the Kremlin’s ability to sustain its war efforts.
In June 2025, Russia’s oil export earnings rose slightly to $13.6 billion due to a temporary price spike triggered by the Israel-Iran conflict, pushing Russian crude prices to ~$60 per barrel. However, prices have since reverted to ~$50-55 per barrel, and are expected to remain at these levels through 2025 and beyond. As a result, oil and gas budget revenues in May-June were 35% lower than the same period in 2024, exacerbating fiscal strains.
The federal budget deficit reached 3.7 trillion rubles in the first half of 2025 — 97% of the full-year target of 3.8 trillion rubles. This is over five times larger than the H1 2024 deficit and 57% higher than the largest H1 deficit in recent years (2023). With oil prices unlikely to recover significantly, Russia is set to miss its budget target by a wide margin, increasing reliance on the National Welfare Fund (NWF) and domestic debt issuance.
The NWF’s liquid assets are under pressure, with Russia expected to draw heavily on these reserves by year-end. In H1 2025, the Ministry of Finance issued 2.3 trillion rubles in OFZ bonds — 90% more than in H1 2024 and 48% of the annual issuance plan. Strong demand for OFZs among Russian banks, coupled with falling yields, suggests expectations of further rate cuts by the Central Bank of Russia (CBR).
Inflation has moderated to 9.4% y-o-y in June, down from ~10% earlier in 2025, due to the CBR’s tight monetary policy. As its tight policy put a heavy burden on the economy, the central bank has cut rates by 300 bps (to 18%) However, persistent issues such as high budget deficits and a tight labor market continue to fuel price pressures, creating tensions between the CBR’s price stability goals and the Ministry of Finance’s war-financing objectives.
Economic growth is faltering, with real GDP contracting by 0.6% quarter-over-quarter in Q1 2025, placing Russia on the brink of recession. Constraints in labor and capital are expected to suppress growth significantly in 2025, further straining the budget and limiting economic momentum.
